The need to keep information generated by businesses and individuals in confidence through security measures has become an increased area of focus in the IT Industry. In the past few years, the need for stronger encryption to meet computer security demand has been debated to a great extent and this will continue in the near future.
This encryption survey study has been carried out in Malaysia to provide insights to decision makers and managers on perceptions and awareness level amongst local current users, potential users and non-users of encryption products.
This in-depth study also provides valuable regional perspective that will help you to build opportunity profiles of the Asian economies.
Some key points to be highlighted in the scope of study: -
- A segmentation of business users by industry categories using encryption products for confidentiality of sensitive information
- Awareness levels amongst the 3 different groups of users: Current, potential & non-users
- Common reasons cited by current users, potential users and non-users for adopting IT security & encryption solutions
- What are the decision making process before purchasing encryption solutions?
- What are the challenges facing the encryption technology in Malaysia?
- List of major countries with the highest adoption levels
- How encryption providers market their products in Malaysia (Pricing, packaging, branding, market segmentation)
- Analysis & profiling of key local vendors
- Coverage of encryption key lengths provided by vendors in Malaysia
- An overview of the Malaysian legislation on encryption and restrictions
Table Of Content
Executive Summary
Overview Of It Security
An overview of encryption
Report overview
Methodology
A Survey On Current Users
Business categories
Reasons for using encryption products
Current usage for encryption and other IT Security products
Other security products used
Estimated annual budget for IT Security
Correlation between key lengths, satisfaction levels and annual budget allocations
The decision making process
A Survey On Potential Users
Business categories
Reasons for having an intention to use encryption products
Current usage of IT Security
Correlation between budget, intensiveness and perceived importance levels of IT Security
Decision making process
A Survey On Non-Users
Business category
Reasons for not using encryption products
Other IT Security products used besides encryption
The decision making process
Survey Conclusion
User segmentation
An Overview Of Global Users Category
Category Of Encryption Providers: Niche Market
Global Vendors Overview
Local Vendors Analysis
Findings
Average Costing
Challenges Of Encryption
International Legislation
Malaysian Legislation
Future Outlook
Appendix 1: Abbreviations
Appendix 2: Vendors Profile In Malaysia
List Of Tables
Table 1: The advantages and disadvantages of PKI (Public Key Infrastructure)
Table 2: The advantage and disadvantage of Secret Key System
Table 3: Respondents category and group
Table 4: Breakdown of current users by industry category
Table 5: Frequency of reasons for using encryption products by current users
Table 6: Frequency of key length encryption usage by current users
Table 7: Important attributes that influence selection and evaluation of IT Security product for current users
Table 8: Breakdown of potential users by industry category
Table 9: Frequency of reasons mentioned for having intention to use encryption products potential users
Table 10: Breakdown of companies by industry category preparing for E- commerce
Table 11: Important attributes that influence the selection and evaluation of IT Security by potential users
Table 12: Awareness of IT Security brands in the market for potential users
Table 13: Awareness of IT Security provider in the market for potential users
Table 14: Breakdown of non-users by industry category
Table 15: Importance attributes that influence selection and evaluation of IT Security product by non-users
Table 16: Quadrant classification
Table 17: Demands of cryptosystem in sectors of major countries key players
Table 18: Worldwide encryption vendors
Table 19: Profiles of encryption vendors in Malaysia as of year 2001
Table 20: Worldwide encryption export and import regulation
List Of Figures
Figure 1: Satisfaction level of current encryption product users (%)
Figure 2: Usage intensiveness level by current users (%)
Figure 3: Current users estimated annual budget for IT Security as at Year 2000
Figure 4: Ranking of how users obtained knowledge information on IT Security product
Figure 5: Usage intensiveness level by potential users (%)
Figure 6: Importance of IT Security by potential sers
Figure 7: Potential users estimated annual budget for IT Security as at Year 2000
Figure 8: Importance of IT Security products by non-users (%)
Figure 9: Usage Intensity Level by Non-Users (%)
Figure 10: Non-Users Estimated Annual IT Security Budget as at Year 2000
Figure 11: Level of Awareness on IT Security Products by Non-Users (%)
Figure 12: Possible Companies that Falls Under these Quadrantds
Findings
The major Malaysian vendors who offer encryption products include RSA Security (M) Sdn Bhd, Computer Associates Sdn. Bhd., Digicert Malaysia Sdn. Bhd., MPT Pacific Technology Sdn. Bhd., Silicon Communications (M) Sdn. Bhd. and Camtech Asia IT & T Sdn. Bhd. The majority of the players (such as RSA Security and Computer Associates) are foreign-owned and have already carved out a niche in the domestic market. RSA (Security Dynamics) is one of the leading players in the IT security and encryption market.
Other IT security products available include Desktop Privacy Software (offered as "Shareware" and "Freeware"). Software encryption is also spreading through the Internet. The prices of this software range from USD 10 to USD 100. Some companies are offering free downloads on the web to anyone not restricted by export regulations.
Malaysian Legislation
- DSA (Digital Signature Act) 1997
Article 79 of the Digital Signature Act 1997 requires people during a search, to give access to computerized data, whether stored in a computer or otherwise. This includes providing the necessary password, encryption code, decryption code, software or hardware required, in order to gain access to computerized data.
Those who refused to follow this act will be fined a maximum amount of RM200, 000 and/or four years of imprisonment (Article 83).
Table 3: Respondents Category and Group|
CATEGORY 1: |
|
|
· Local users of · Local potential · Local non-user of |
· Local market
|
Table 5: Frequency of reasons for using encryption
products by current users
|
REASONS MENTIONED |
FREQUENCY OF |
|
My vendor recommended it |
0 |
|
Everyone else is using it |
2 |
|
We need it |
7 |
|
As a precaution |
3 |
|
It is an industrial standard |
1 |
|
Business partner s requirement (business standardization) |
1 |
|
It reflects our company's standard |
1 |
Table 11: Important attributes that influence the selection
and evaluation of IT Security by potential users
|
|
WEIGHTED AVERAGE IMPORTANCE |
|
Price |
19 |
|
User-friendliness |
16 |
|
Function |
21 |
|
After sales support |
21 |
|
Relationship with supplier |
12 |
|
High tech features |
1 |
*Note: Respondents were asked to rate each of the attributes above.
Scores above zero indicate that the factor is considered important
by the decision-makers. The higher the score is, the more it
influences the decision-making. Zero is neutral score where the
factor is seemed to be neither important nor unimportant. A score
below zero (negative score) indicates that the factor is not
important, whereas the lower the score, the more unimportant
it is towards the decision-making process.
Figure 3: Current users estimated annual budget for IT
security as at Year 2000
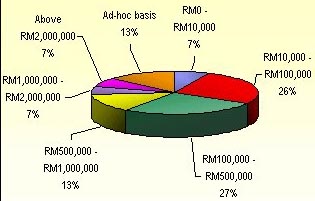
Source: © 2001 iMonitorTM All Rights Reserved
Figure 9: Usage Intensity Level by Non-Users (%)
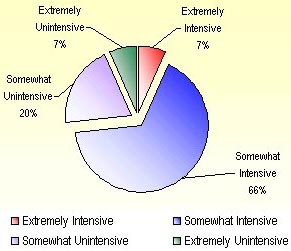
Source: © 2001 iMonitorTM All Rights Reserved