1. What are Employee Stock Options Plans (ESOPs) and Stock Appreciation Rights (SARs)?
- ESOPs are a stock option provided by a company
to its employees, to purchase its shares on future dates and at a
pre-determined price. They are basically a form of incentive given
out by a company to its employee basis their contribution to the
company. Further, such an incentive helps the company to motivate
its employees to contribute to the growth and profitability of the
company in future as well.
ESOPs are defined under Section 2(37) of Companies Act, 2013 (CA 2013) and are governed by Section 2(37) read with Section 62(1)(b) of CA 2013 along with Rule 12 of the Companies (Share Capital and Debentures) Rules 2014.
There is a minimum vesting period of one year between the grant of options and vesting of option, as per the Regulation No 9 of the SEBI Guidelines, 1999 further, it is to be noted that, as such, there is no such lock-in period involved in ESOPs and the issuing company/employer is at liberty to specify the lockin period for the shares issued pursuant to exercise of option.
- SARs are instruments issued and used by a
conglomerate for making stock-based compensation. SARs are
alternatives to Employee Stock Option/Purchase Plans/Schemes
(ESOPS/ESPS), which are equity based. It may also be called a form
of bonus compensation given to employees that is equal to the
appreciation of company stock over an established time, but without
employee being paying the exercise price.
Depending on the contractual terms of the respective employee with his employer, SARs are of can be following two types 'equity settled' and 'cash settled'. SARs which are settled by way of shares of a company are called as equity settled SARs whereas a SAR which entitles an employee the right to receive cash payments after a specific period of time or upon fulfilment of specific criteria is called as cash settled SARs.
A company is needed to make a provision in its P&L account each year, depending on how the price of shares vary each year, but this option of compensation to employees may not be suitable to companies which are not cash rich. While the CA 2013 has prescribed rules for issuance of shares to employees under Stock Plans, it is silent on the grant and exercise of SARs including issuance of equity settled SARs and Phantom Stock Options or Cash Settled SARs.
The companies by issuing SARs contemplate to pass on the appreciation in the value of a certain number of equity shares to their employees in the value of a certain number of equity shares to their employees, unlike ESOPs. The company is also saved from diluting its rights as a result of which its shareholding remains unaltered. The primary benefit to the employee, that comes with SARs, is that the employee can receive proceeds from stock price increases without being required to buy anything outright.
2. What are the stages involving the process of issuance of ESOPS? What are the key phases relating to SARs?
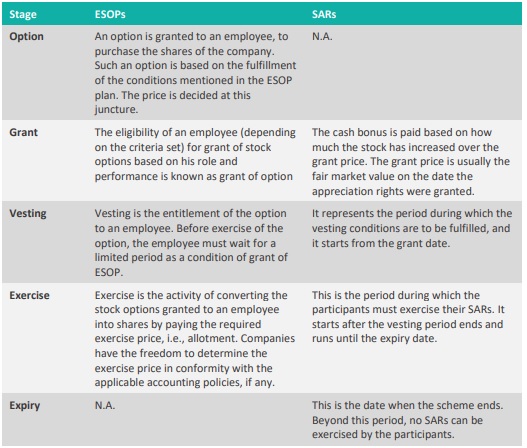
3. Which provisions of Income Tax Act, 1961 govern ESOPs and SARs transactions? ESOPs
Prior to the Finance Act, 2009, ESOPs were covered under the Fringe Benefit Tax (FBT), but thereafter they have been made taxable at the hands of the employee as 'perquisites', subject to certain conditions. Relevant provisions under the ITA, which deal with ESOPs and gains from their redemption are set out as under.
- Section 17 – "Salary",
"perquisite" and "profits in lieu of salary"
defined.
- (2)(iii) the value of any benefit or amenity
granted or provided free of cost or at concessional rate in any of
the following cases—
- by a company to an employee who is a director thereof;
- by a company to an employee being a person who has a substantial interest in the company;
- by any employer (including a company) to an employee to whom the provisions of paragraphs (a) and (b) of this sub-clause do not apply and whose income under the head "Salaries" (whether due from, or paid or allowed by, one or more employers), exclusive of the value of all benefits or amenities not provided for by way of monetary payment, exceeds fifty thousand rupees:
- (2)(vi) the value of any specified security or
sweat equity shares allotted or transferred, directly or
indirectly, by the employer, or former employer, free of cost or at
concessional rate to the assessee.
Explanation – For the purposes of this sub-clause -- "specified security" means the securities as defined in clause (h) of section 2 of the Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act, 1956 (42 of 1956) and, where employees' stock option has been granted under any plan or scheme therefor, includes the securities offered under such plan or scheme;
- "sweat equity shares" means equity shares issued by a company to its employees or directors at a discount or for consideration other than cash for providing know-how or making available rights in the nature of intellectual property rights or value additions, by whatever name called;
- the value of any specified security or sweat equity shares shall be the fair market value of the specified security or sweat equity shares, as the case may be, on the date on which the option is exercised by the assessee as reduced by the amount actually paid by, or recovered from, the assessee in respect of such security or shares;
- "fair market value" means the value determined in accordance with the method as may be prescribed;
- "option" means a right but not an obligation granted to an employee to apply for the specified security or sweat equity shares at a predetermined price;
- (2)(iii) the value of any benefit or amenity
granted or provided free of cost or at concessional rate in any of
the following cases—
To read the full article click here
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.


