New electric vehicle (EV) registrations grew 23 percent in 2023, down from the 52 percent growth seen the year prior, furthering concerns about slowing growth. Regulators and CEOs are expressing apprehension regarding the plans of Chinese automakers to expand into North America. Stellantis announced a 10 percent decrease to profit in the second half of 2023 compared to the prior year, citing International Union, United Automobile, Aerospace and Agricultural Implement Workers of America (UAW) strikes and associated higher salaries and employee benefits as the cause of the decrease.
In regulatory news, the Environmental Protection Agency rolls back dramatic proposed regulations mandating reductions on tailpipe emissions. Robotaxi industry leader Waymo seeks approval to expand its presence in California, looking beyond San Francisco.
Additional February insights are included below.
Industry Update
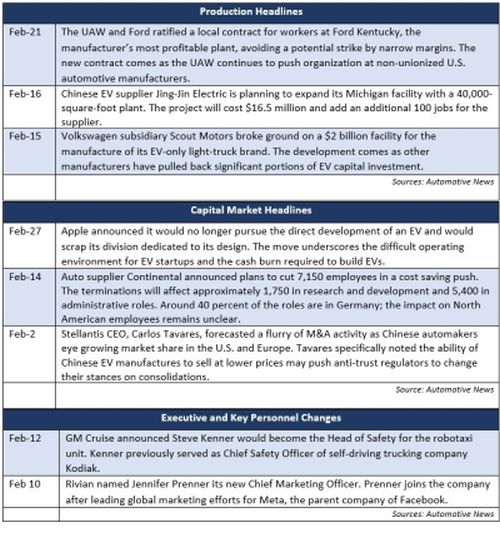
January inventory levels ended at 2.39 million units, a 93,000 unit decrease from December. Days' supply (DS) closed at 39, approximately 5 percent below the five-year average and a slight improvement over the last several months. Inventory at Detroit's Big Three led the way for the U.S., with a 26,000-unit increase in light truck inventory for GM.
January U.S. light vehicle sales decreased approximately 1.3 percent year over year, missing Bloomberg consensus estimates. Vehicle mix continues to remain near record levels, trending toward large vehicles, as average transaction prices remain steady but elevated compared to this time last year. Expectations for the full year 2024 remain moderate based on pent-up demand caused by inventory shortages.
Industry Focus — The Year Ahead for EVs
The EV industry in the U.S. has experienced a significant slowdown in growth during the last year, highlighted by changes in go-to-market strategies and capital deployment plans for major automakers. This slowdown has raised questions about the trajectory of EV consumer adoption and cast a stark light on the factors influencing consumer behavior. Specifically, a critical lack of EV options priced for the mass market paired with a limited outlook on new models available to consumers paints a challenging picture for EVs in 2024.
Growth Slows, but the Market Marches On
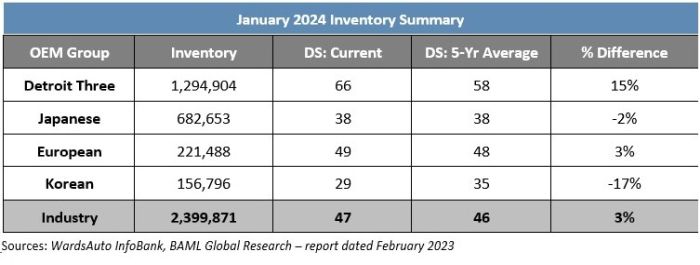
A recent Cox Automotive study showed more than 1.2 million EVs were sold in the U.S. last year, bringing EV market share to 7.6 percent in 2023 compared to 5.9 percent in 2022. While the overall EV market is still growing, growth is slowing — fourth quarter EV sales grew 40 percent in Q4 2023 compared to 59 percent in Q4 2022. While stronger inventory, improved leasing infrastructure and generally stronger sales efforts will support further EV growth, price remains a significant limiting factor for consumers.
Priced Out of the Market?
The same Cox Automotive study estimated the average price a consumer paid for an EV in December 2023 was just over $50,000 — nearly 5 percent higher than traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. U.S. car buyers have limited options under $40,000: only the Chevrolet Bolt and Volkswagen ID4.
The lack of lower-cost options has contributed to consumer perception of EVs as a luxury item — a perception that stands in contrast to automaker and federal government messaging about broader adoption of EVs. The issue of vehicle pricing is not lost on automakers, and in fact has contributed to a 'price war' in the last 12 months between EV manufacturers in the U.S., with average transaction prices for Tesla EVs declining by nearly 20 percent compared to last year and all EVs experiencing an 11 percent decline in prices.
These price reductions signal a concerted effort by manufacturers to attract consumers and stimulate demand in a market where affordability becomes more of a key concern, as early adopters were willing to pay the higher prices. There's a downside to these price reductions, however. Reduced prices for new vehicles impact used vehicle prices, which in turn impacts residual values and drives leasing costs higher for consumers.
Additionally, the complexities of global production dynamics, exemplified by EV manufacturer BYD's exploration of production facilities in Mexico to avoid 27.5 percent U.S. tariffs, add another layer of uncertainty to the equation. As manufacturers navigate the intricacies of international trade, including tariffs and trade treaties, customers may delay purchasing decisions to capitalize on potential price drops, impacting dealers' inventory strategies.
Persistent Hybrid Demand
Notably light in existing vehicle lineups (and future development plans) for U.S. automakers are hybrid vehicles. Generally priced more comparably with ICE vehicles than EVs, hybrids are a long-standing first step toward zero emission vehicles (ZEV) for consumers and automakers alike. Representing 8.3 percent of the U.S. auto market in 2023 (up from 5.5 percent in 2022) hybrids saw significant growth in the U.S. last year. Ford saw its sales of hybrid vehicles grow nearly 25 percent on the year.
While affordability and range anxiety make hybrids a compelling option for consumers looking for a reduced emissions vehicle, they are also an attractive first step for automakers looking for profitability in their reduced-emissions segments. Ford has indicated that, in its slowdown of investment for EVs, it will lean more heavily on its hybrid units for emissions requirements and customer demand while Toyota has indicated its highly profitable hybrid business will be a key pillar in funding its EV development.
Limited Introduction of New Models and Production Adjustments
Detroit's Big Three are not particularly well positioned for meeting customer demands with expanding EV product lines and mass market pricing. With a very limited number of new models launching in the U.S. in the next two years, the automakers' product pipelines seem to have preemptively reflected their clawed-back investment track.
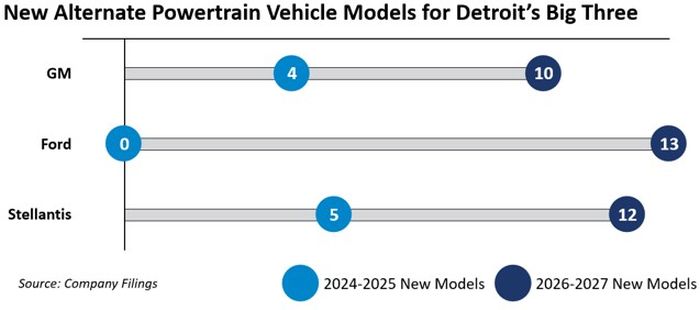
Furthermore, of the 44 new alternative powertrain vehicles the Big Three plan to introduce through 2027, only six are planned as hybrid models — one for GM, one for Stellantis, and four for Ford.
GM recently announced its plans to revive the Bolt, its low-cost mass market EV that was previously scheduled to be shuttered to ramp up production of EV trucks. While production was ramped down fully in 2023, the company expects to bring production fully back online in 2025 using new lithium-ion phosphate battery cells. The Bolt represented more than 82 percent of GM's EV unit deliveries in 2023.
Regulatory Landscape
The EPA Eases Proposed Tailpipe Emission Standards: An earlier proposal from the EPA called for a 56 percent reduction in new vehicle emissions by 2032 and for EVs to represent 60 percent of new vehicle production by 2030. The new plan calls for less drastic standards through 2030 with a steeper ramp-up from 2030 to 2032.
California Regulators Postpone Waymo Expansion Decision: Robotaxi company Waymo sought authorization to expand outside of San Francisco to other cities in California. State regulators have until June 19, 2024, to approve or deny the proposal. The decision comes amidst increased scrutiny of self-driving taxis due to recent incidents involving pedestrians for both Waymo and Cruise, with the Cruise incident resulting in the company's operating license being suspended in California.
Cadillac Lyriq Regains Eligibility for Federal Tax Credit: Buyers of the EV lost the tax credit on January 1, 2024, due to two components failing to meet battery sourcing rules. The automaker announced that the Lyriq was in full compliance in February.
Originally Published 29 February 2024
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.



