1 Relevant Authorities and Legislation
1.1 Which entities regulate what type of gambling and social/skill gaming activity in your jurisdiction?
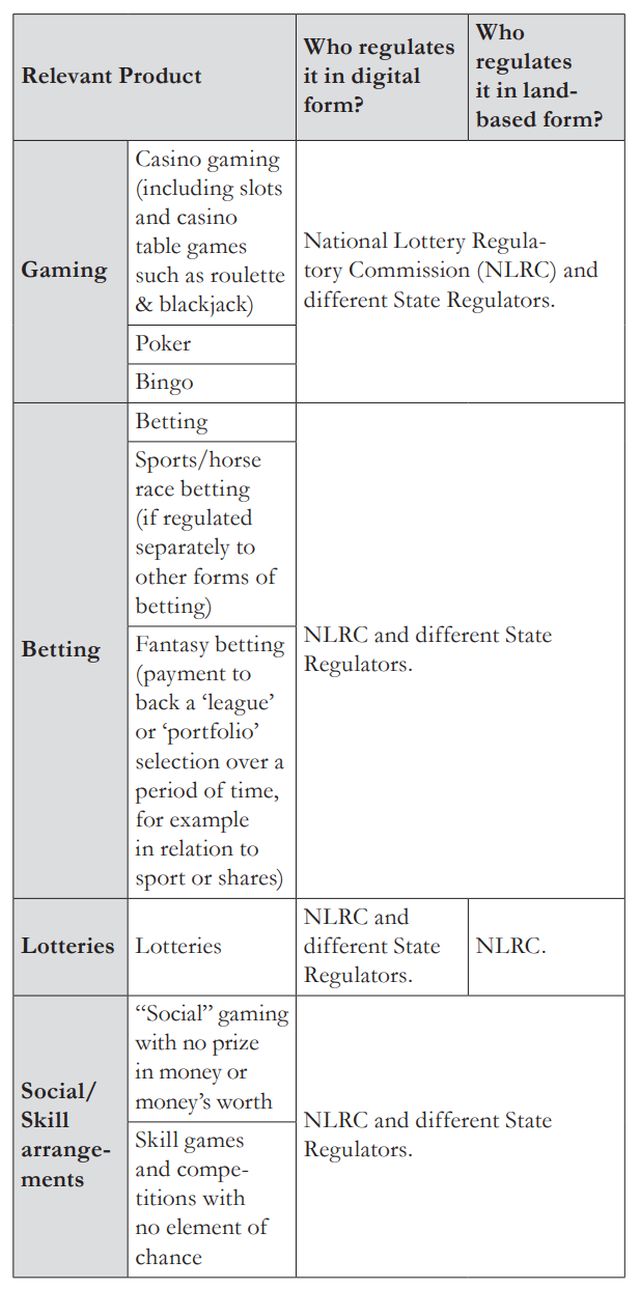
1.2 Specify: (i) the law and regulation that applies to the Relevant Products in your jurisdiction; and (ii) – in broad terms – whether it permits or prohibits the offer of Relevant Products to persons located in your jurisdiction.
Each product licence operates within a legal framework that reflects a mix of federal- and state-level regulations. An operator seeking to operate under a product licence must comply with both direct and indirect regulations. The National Lottery Act 2005 and the National Lottery Regulation 2007 establish the overarching guidelines, while other pieces of legislation, such as the Casino and Gaming Machines (Prohibition) Act 1977, Casino Taxation Act, Companies and Allied Matters Act 2020, Criminal Code of Nigeria, Federal Competition and Consumer Protection Act (FCCPA), Data Protection Act 2023, Central Bank of Nigeria Act 2007 and Finance Act 2023, contain provisions that regulate the activities of the Relevant Products. At the state level, each state in Nigeria controls the activities of the Relevant Products within its borders by the establishment of relevant regulatory bodies such as the Lagos State Lottery Board and Oyo State Lottery Board. The gaming or tax laws of the various sub-nationals regulate the affairs of gaming in the state.
In contrast, state governments possess authority over the authorisation and licensing of lottery and gaming activities within their respective jurisdictions. While the national government sets the overall regulatory framework, states play a crucial role in granting licences to operators. State governments may establish their regulatory bodies or commissions to oversee the licensing process, reflecting the decentralised nature of gambling regulation in Nigeria.
Generally, the National Lottery Act 2005 permits individuals in Nigeria to engage in gaming, betting and lotteries. However, it is important to note that the NLRC only allows land-based casinos.
2 Application for a Licence and Licence Restrictions
2.1 What regulatory licences, permits, authorisations or other official approvals (collectively, "Licences") are required for the lawful offer of the Relevant Products to persons located in your jurisdiction?
A person who wishes to operate under any of the Relevant Products must make an application to the NLRC. The NLRC is responsible for issuing different kinds of licences depending on the gaming activity that the applicant intends to go into such as:
- Lottery permits.
- Sports betting licences.
- Promotional permits (CSPs).
2.2 Where Licences are available, please outline the structure of the relevant licensing regime.
The NLRC has a governing body that oversees the affairs of the Commission through the Director General and 15 states. The NLRC is made up of different divisions charged with different responsibilities such as licensing, monitoring, advisory compliance, surveillance and enforcement and dispute resolution, etc.
2.3 What is the process of applying for a Licence for a Relevant Product?
Anyone who wishes to conduct any form of gaming must apply to the NLRC. The application for each class of licence differs, and the applicant must abide by the requirements relevant to its proposed scheme.
- An application must be made to the regulatory authority in the jurisdiction or state in which the applicant/operator wishes to conduct its operations.
- The application must consist of the following:
- an application letter;
- a non-refundable application fee (prescribed by the regulatory authority);
- documentary evidence of business incorporation;
- a detailed business plan or proposal of the proposed gambling operations;
- the applicant's financial capability, certified software and trade mark; and
- a drawing of the applicant's software architecture along with a service-level agreement between the operator and software operator; and
- a bank guarantee.
- Upon the submission of the application, the regulatory authority may decide to undertake a due diligence visit to the applicant's principal place of business before it decides on whether to grant a licence to the operator.
There is no difference between application requirements for land-based and online operators. They both take the same format and require similar conditions to be fulfilled by the applicant/operator.
2.4 Are any restrictions placed upon licensees in your jurisdiction?
While there is no express limitation on licensees, licensees must follow the NLRC's rules and regulations, which include responsible gaming practices, data protection safeguards, advertising guidelines, and more.
Responsible gambling measures: Nigeria's gaming and betting laws highlight the necessity of safe gambling activities. Licensees must employ anti-underage gaming measures such as reliable age verification methods. They must also give self-exclusion options, deposit restrictions and contact information for responsible gambling helplines. To ensure consumer protection, the NLRC checks compliance with these procedures
Advertising regulations: regulations govern the promotion and advertising of gambling (gaming) and betting services. Operators must follow the NLRC's content, location and targeting requirements for their adverts. The goal is to safeguard vulnerable persons from excessive exposure to gambling-related content by preventing fraudulent or deceptive advertising.
Enforcement and penalties: the NLRC is in charge of enforcing gaming and betting rules in Nigeria in partnership with law enforcement authorities. Non-compliance with the regulations can result in penalties such as penalty fees, suspension of licences or revocation, and, in certain situations, criminal prosecution. The NLRC has the jurisdiction to investigate complaints and prosecute operators who contravene regulatory standards.
To view the full article, click here.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.


